How Do They Work?
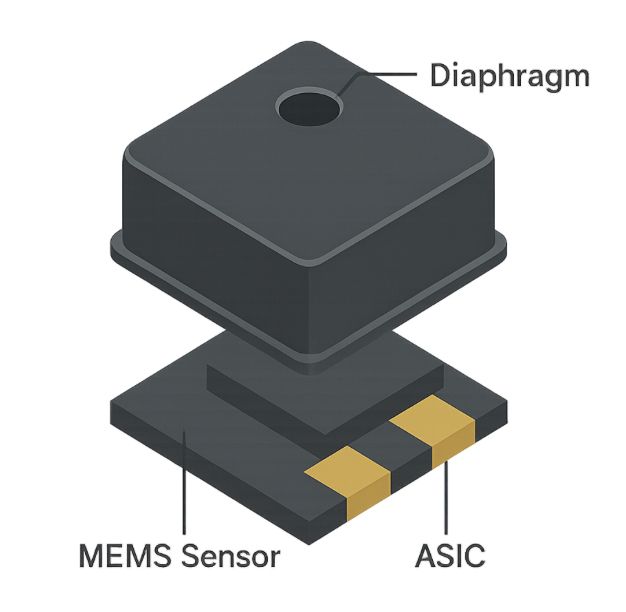
At the core of a MEMS microphone is a tiny diaphragm that moves in response to sound waves. This movement changes the electrical signal, converting acoustic energy into a digital or analog signal—just like traditional microphones, but on a much smaller scale.
These mics typically include:
- A MEMS sensor that detects sound
- An ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) that processes and amplifies the signal
- A small, sealed housing that protects the components from dust, moisture, and vibration

In the field with the Instamic Pro Plus C
Why Use MEMS Microphones?
MEMS microphones have quickly become a go-to solution for compact, wireless, and mobile audio applications due to several key advantages:
- Small & Lightweight: Ideal for wearables, smartphones, and stealthy audio gear
- Low Power Consumption: Perfect for battery-powered devices
- High Consistency: Precision manufacturing ensures tight tolerances and reliability
- Durable: Resistant to shock, vibration, and environmental factors
- Omnidirectional Capability: Excellent for capturing ambient or environmental audio

MEMS mics are everywhere—from phones and smart speakers to action cams, hearing aids, and pro audio gear like Instamic. Their small footprint and rock-solid performance make them ideal for creators and engineers who need quality audio without bulky setups.
